As Republicans continue to cover up their repeated votes to eliminate and gut coverage for pre-existing conditions, several are claiming that “high risk pools” are the answer. The reality is that high risk pools have never worked to protect people with preexisting conditions — every time they have been tried, they have failed. Here’s why.
HIGH RISK POOLS IMPOSE HIGH PREMIUMS & DEDUCTIBLES …
Premiums For Coverage In High Risk Pools Were As Much As 200 Percent Higher Than The Average Rate But Covered Less Care. “High-risk pool enrollees faced substantially higher premiums than people in the normal individual market, often by as much as 150 percent to 200 percent, although some pools did offer subsidies to low-income enrollees…And stunningly, the overwhelming majority of state high-risk pools actually refused to pay for services associated with a patient’s pre-existing conditions in the first months of their enrollment.” [Center for American Progress, 2/16/17]
Deductibles For High Risk Pool Enrollees Were Well Above Maximum Allowed By ACA. ”Fourteen states had plans with deductibles of $10,000 per year or higher, substantially greater than the current maximum $7,150 deductible for catastrophic plans in the marketplaces. Thirty states imposed maximum lifetime limits; others had annual coverage limits as low as $75,000 per year.” [Commonwealth Fund, 3/29/17]
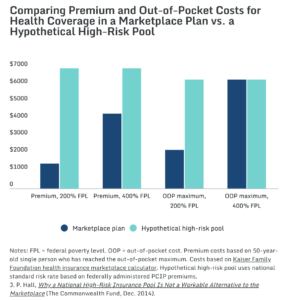
Source: Commonwealth Fund, 3/24/17
… COST TAXPAYERS MORE …
Despite High Premiums, High Risk Pools Could Still Cost The American People Over $90 Billion Annually. “The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) recently estimated that up to 17,875,000 people with preexisting conditions were uninsured in 2010. Had all of them been covered by high-risk pools, the cost would have been $194.8 billion in 2010 dollars, with premiums covering only $103.3 billion. Thus, states and the federal government would have needed to find $91.5 billion in additional funding to cover them all—much more than the up to $10 billion per year in federal assistance to states recently proposed by congressional Republicans.” [Commonwealth Fund, 3/29/17]
An Analysis Of High Risk Pools Under The ACHA Finds Such Pools Would Cost The Government Between $37 and $56 Billion Annually. “Government costs for supporting the high-risk pool using ACA-like coverage and subsidies would range from $37 to $56 billion in 2020 and $437 to $656 billion over 10 years (2020–2029), depending upon the eligibility rules used.” [The Urban Institute, May 2017]
Even Conservatives Estimated High Risk Pools Would Cost $15-$20 Billion Annually. “For comparison, conservative experts James Capretta and Tom Miller have estimated that $15 billion to $20 billion per year, or $150 billion to $200 billion over 10 years, would be needed to fully finance high-risk pools even if they covered only 2 million to 4 million people.” [Center For American Progress, 2/16/17]
Premiums For High Risk Pool Coverage Paid Just 53 Percent Of Program Costs. “Premiums ranged from 125 percent to 200 percent of average premiums in the individual market, yet covered only about 53 percent of claims and administrative costs nationally (Wisconsin allowed premiums up to 200 percent of average).” [Commonwealth Fund, 3/29/17]
… AND RESTRICT COVERAGE
High Risk Pools Typically Had Pre-Existing Condition Exclusions And Limited Benefits. “Many such pools had pre-existing condition exclusion periods, limited benefits, and enrollment limits; all of these characteristics served to reduce the value of the coverage, creating high financial burdens for enrollees and limiting the number of people who could access the coverage.” [Health Affairs, 3/15/16]
Most State High Risk Pools Had Lifetime And Annual Limits On Coverage. “Thirty-three pools [out of 35 states] imposed lifetime dollar limits on covered services, most ranging from $1 million to $2 million. In addition, six pools imposed annual dollar limits on all covered services while 13 others imposed annual dollar limits on specific benefits such as prescription drugs, mental health treatment, or rehabilitation.” [Kaiser Family Foundation, 2/22/17
High Risk Pools Typically Had Waiting Periods. “There were 35 state high-risk pools before the Affordable Care Act passed. To control costs, they would often do things like charge higher premiums than the individual market. Most had waiting periods before they would pay claims on members’ preexisting conditions, meaning a cancer patient would need to pay premiums for six months or a year before the high-risk pool would cover her chemotherapy treatments.” [Vox, 5/3/17]
High Risk Pools Mean Delayed Or Forgone Care. “Even once they were in a high-risk pool, the high costs and limited benefits prompted some people to delay or forgo care, leading to poorer health outcomes and even more spending. And many families accrued substantial medical debt, even with the coverage.” [Stateline, 2/16/17]
HIGH RISK POOL = MORE PEOPLE UNINSURED
Limited Coverage And High Costs Cause People To Remain Uninsured. “Some patients also delayed care to save money, exacerbating their health conditions, and only entered the pools when their conditions became emergencies.” [Stateline, 2/16/17]
CMS: One-Third Of Uninsurable Were Unable To Afford High Risk Pool Coverage. A 2004-05 study by the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services found that “nationally, high-risk pool premiums are above 25 percent of family income (i.e., are unaffordable) for 10 percent of all individuals, 18 percent of the uninsured, and 29 percent of the uninsurable. By these standards, almost one-third of the uninsurable are unable to afford high-risk pool coverage…” [CMS, Health Care Financing Review, Winter 2004-2005]
As Evidenced By Wisconsin’s Health Insurance Risk-Sharing Plan (HIRSP), High Risk Pools Offer Less Protection For Fewer People Than Does The Affordable Care Act.“HIRSP, which covered people with pre-existing health conditions before the Affordable Care Act, was one of the largest and most successful so-called high-risk pools in the country. But at its peak it covered only an estimated 24,000 people, and those were people who could afford health insurance. ‘It didn’t begin to catch all the people who needed it,’ said Pollitz of the Kaiser Family Foundation. Mahaffey echoed Pollitz’s assessment. ‘If you bring HIRSP back, it may help a small segment of the population,’ she said, ‘but nowhere near what the Affordable Care Act is serving.’” [Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, 9/20/18]
HIGH RISK POOLS HAVE BEEN TRIED & FAILED
States Sharply Restricted Enrollment In High-Risk Pools, Resulting In Only About Five Percent Of Those Eligible For High Risk Pools To Enroll In 2008. “States sharply restricted enrollment, set premiums further above what many families could afford, and/or scaled back coverage (such as by cutting benefits, raising deductibles and other cost sharing, imposing waiting periods for coverage of pre-existing conditions, and establishing lifetime dollar limits on benefits). Only 226,000 people in 35 states were enrolled in high-risk pools in 2011, on average. In 2008, only about 5 percent of those estimated to be eligible for those high-risk pools (because they had a chronic condition and were uninsured) were enrolled.” [Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, 11/17/16]
California High Risk Pool Led To Waiting Lists, High Premiums, And Lifetime Limits. “For example, California’s high-risk pool imposed a shorter-than-average, three-month waiting period before enrollees could receive treatment for pre-existing conditions—but also imposed a $75,000 annual limit on benefits along with a $750,000 lifetime limit. In addition, the state capped enrollment, resulting in long waiting lists of people unable to enroll; at the same time, the pool’s high premiums proved difficult for enrollees to afford, leading some to drop out.” [Center for American Progress, 2/16/17]
Premiums in Florida’s High Risk Pool Were Twice The Normal Rate. “Many states starved high-risk pools of cash. Florida’s contained only about 200 people in 2011. Premiums were commonly twice the normal rate. Many states had enrolment caps, meaning that even people willing to fork over were not guaranteed coverage.” [The Economist, 1/16/17]
In Wisconsin, “Cancer Doesn’t Wait” For High Risk Pool Waiting Periods. “The benefit waiting periods used by Wisconsin’s and other states’ high-risk pools are a big concern for patient advocates and provider groups. ‘A six-month exclusionary period is a serious issue,’ said Dr. Len Lichtenfeld, deputy chief medical officer for the American Cancer Society, who also testified at the House hearing. ‘Cancer doesn’t wait.’” [Modern Healthcare, 2/13/17]
In Utah, High Risk Pools Were Limited In Size, And Offered Sub-Par, Delayed Coverage. “Stevenson said only 3,000 people signed up for Utah’s risk pool plan while 200,000 Utahns are signed up for insurance through Obamacare. ‘Utah’s past high risk pool plan had many limitations too,’ he said. People with pre-existing conditions had to wait six months before using their coverage. Pregnant women had a 10 month waiting period before they had any coverage for them or their baby. ‘The measure of success for a program is how many people it helps and if you are only covering 3,000 people and leaving tens of thousands uninsured, I don’t think that’s a good thing to go back to,’ he said.” [CBS KUTV, 3/9/17]
High Risk Pools Mean Higher Costs, Higher Uninsured, And Less Coverage. “The reality is that high-risk pool coverage was prohibitively expensive and there is little evidence to suggest that the existence of such pools made coverage less costly for others in the individual insurance market. Without substantially more federal funding than currently proposed, these facts are not likely to change. People with preexisting conditions may have “access” to coverage, but most will not be able to afford it and those who can will face limited benefits and extremely high deductibles and out-of-pocket payments.” [Commonwealth Fund, 3/29/17]

